The average depth of the Indian ocean is about 3000m. The value of fractional compression of water at the bottom of the ocean is _____
(given that bulk modulus of water is \(2.2\times 10^9 Nm^{-2}\) ,\(g=9.8\) ,\(\rho_{H_2O}=1000kg.m^{-3}\) )
(a) \(3.4 \times 10^{-2}\)
(b) \(1.34\times 10^{-2}\)
(c) \(4.13\times 10^{-2}\)
(d) \(13.4\times 10^{-2}\)
The fractional compression or decrease in volume
\(\frac {\triangle V} {V} =\frac {h\rho g} {k}\)
h= average
\(\rho=\) the density of ocean water
g= gravitational acceleration and
k= bulk modulus
\(\frac {\triangle V} {V} =\frac {3\times 10^3\times 10^3 \times 9.8} {2.2.\times 10^9}\)
\(=\frac {3} {2.2}\times 10^{-4}\times 98\) = \(\frac {147} {11} \times 10^{-4}\) = \(=1.34\times 10^{-2}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The value of \(I=\displaystyle \int_{o}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} \frac {(\sin x +\cos x )^2} {\sqrt{1+\sin 2x}}\: dx\) is _______
(a) 2 (b) 1
(c) 0 (d) 3
\(I=\displaystyle \int_{o}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} \frac {(\sin x +\cos x )^2} {\sqrt{1+\sin 2x}} dx\)
\(I=\displaystyle \int_{o}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} \frac {(\sin x +\cos x )^2} {\sqrt{\sin^2 x +\cos^2 x+2\sin x \cos x}} dx\)
\(I=\displaystyle \int_{o}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} \frac {(\sin x +\cos x )^2} {\sqrt{\sin x+\cos x)}^2} dx\)
\(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} (\sin x +\cos x) dx\)
\(\Big(\frac {\cos x} {-1}+\sin x\Big)_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}}=1-(-1)=2\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A body of mass m is accelerated niformly from rest to a speed V in a time T. The instantaneous power delivered to the dody as a function of time is given by ________
(a) \(\frac 1 2 \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t\)
(b) \(\frac 1 2 \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t^2\)
(c) \( \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t\)
(d) \( \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t^2\)
Power = Force X velocity
\(= (ma) (v)=(ma) (at)=ma^2t\)
Power = \(m\Big(\frac {V} {T}\Big)^2 (t)\) = \( \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The axis of a parabola is long the line \(y=x\) and the distances of its vertex and focus from origin are \(\sqrt{2} \) and \(2\sqrt{2} \) respectively.If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant.Then the equation of the parabola is ______
(a) \((x+y)^2=(x-y-2)\)
(b) \((x-y)^2=(x-y-2)\)
(c) \((x-y)^2=4(x+y-2)\)
(d) \((x-y)^2=8(x+y-2)\)
Vertex is (1,1)
Focus is (2,2)
directrix x+y=0
Equation of parabola is
\((x-2)^2+(y-2)^2=\Big( \frac {x+y} {\sqrt{2}}\Big)^2\)
\(x^2+y^2-2xy=8(x+y-2)\)
\((x-y)^2=8(x+y-2)\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Let \(f:[0,2]\to R\) be function which is continuous on [0,2] and is differentiable on (0,2) with \(f(0)=1\) .Let \(F(x)=\displaystyle\int_{0}^{x^2} f(\sqrt{t}) dt\) for \(x\in [0,2]\) . If \(F'(x)=f'(x)\) for all \(x\in (0,2)\) then F(2) equals
(a) \(e^2-1\)
(b) \(e^4-1\)
(c) \(e-1\)
(d) \(e^4\)
\(F(x)=\displaystyle\int_{0}^{x^2} f(\sqrt{t}) dt\) for \(x\in [0,2]\)
\(F'(x)=f(x).2x\)
\(F'(x)=f'(x)\: \forall x\in (0,1)\)
\(f(x).2x=f'(x)\)
\(\frac {f'(x)} {f(x)}=2x\)
\(\ln f(x) =x^2+c\)
\(f(x)=e^{x^2+c}=e^{x^2}.e^c\)
\(f(0)=1\Rightarrow1=e^c\)
\(F(x)=\displaystyle \int_{0}^{x^2} e^x\: dx=e^{x^2}-1\)
\(F(2)=e^4-1\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process \(P=P_0\Big[ 1+ \Big( \frac {2V_0} {V}\Big)^2\Big]^{-1}\) where \(P_0,V_0\) are constants.Change in temperature of the gas when volume is changed from \(V=V_0\) to \(V=2V_0\) is _______
(a) \(\frac {4} {5} \frac {P_0V_0} {nR}\)
(b) \(\frac {3} {4} \frac {P_0V_0} {nR}\)
(c) \(\frac {2} {3} \frac {P_0V_0} {nR}\)
(d) \(\frac {7} {9} \frac {P_0V_0} {nR}\)
\(P=P_0\Big[ 1+ \Big( \frac {2V_0} {V}\Big)^2\Big]^{-1}\)
\(V=V_0,P=P_0/5\)
\(T_i=\frac {PV} {nR}=\frac {(P_0/5)V_0} {nR}=\frac {P_0 V_0} {5nR}\)
\(V=2V_0,P=P_0/2\)
\(T_f=\frac {PV} {nR}=\frac {(P_0/2)(2V_0)} {nR}=\frac {P_0 V_0} {nR}\)
\(\triangle T=T_f-T_i=\frac {4P_0V_0} {5nR}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
If \(\displaystyle\int f(x) \cos x \:dx=\frac 1 2 [f(x)]^2 +C\) and \(f(0)=0\) then \(f'(0)=\) ________
(a) 1 (b) -1
(c) 0 (d) 5
we have
\(\displaystyle\int f(x) \cos x \:dx=\frac 1 2 [f(x)]^2 +C\)
on Differentiating w.r.t x
\(f(x) \: \cos x=\frac 1 2\times 2 f(x) .f'(x)\)
\(f(x) \: \cos x= f(x) .f'(x)\)
\(f'(x) =\cos x\)
\(f'(0)=\cos (0)=1\)
\(f'(0)=1\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A fair coin is tossed at a fixed number of times. If the probability of getting exactly 3 heads equals the probability of getting exactly 5 heads, then the probability of getting exactly one head is
________
(A) \(\frac {1} {64}\)
(B) \(\frac {1} {32}\)
(C) \(\frac {1} {16}\)
(D) \(\frac {1} {8}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The transformation due to reflection of (x,y) through the origin is described by the matrix
_____
(A) \(\begin{pmatrix}
-1 & 0 \\
0 & -1
\end{pmatrix}\) (C) \(\begin{pmatrix}
0 & -1 \\
-1 & 0
\end{pmatrix}\)
(B) \(\begin{pmatrix}
-1 & 0 \\
0 & 1
\end{pmatrix}\) (D) \(\begin{pmatrix}
1 & 0 \\
0 & -1
\end{pmatrix}\)
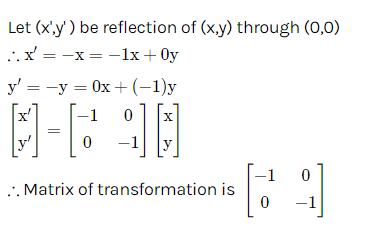
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A gas satisfies the relation \(PV^{5/3}=K\),where P is pressure ,V is volume and K is constant.
The dimension of constant K are_________
(A) \([ML^4 T^{-2}]\)
(B) \([ML^2 T^{-2}]\)
(C) \([ML^6 T^{-2}]\)
(D) \([ML T^{-2}]\)
Given \(PV^{5/3}=K\)
Using dimensional balance method
Dimension of P= \(ML^{-1} T^{-2}\)
Dimenstion of V= \(L^3\)
Dimension of \(V^{5/3}=L^5\)
Dimenstion of LHS=Dimenstion of RHS
dimenstion of K= \([ML^{-1}T^{-2}]\times [L^5]
\)
\(=[ML^4 T^{-2}]\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The Value of the sum \(\displaystyle \sum_{n=1}^{13} (i^n +i^{n+1})\) where \(i=\sqrt{-1}\) equals __________
(A) i
(B) i-1
(C) -i
(D) 0
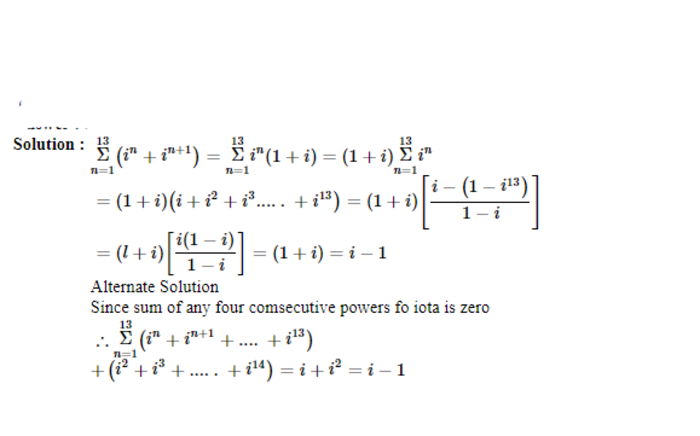
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
which of the following products are formned on hydrolysis of \(NaO_2\)?
(A) NaoH (B) \(H_2O_2\)
(C) \(O_2\) (D) \(H_2O\)
(a) A,D (b) A,C,D
(c) A,B,D (d) A,B,C
On hydrolysis of \(NaO_2\)
( a superoxide of sodium)
It gives \(O_2,H_2O_2\) and NaoH as Products
\(2NaO_2+2H_2O\rightarrow 2NaOH+O_2+H_2O_2\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
If \(\sec 2 \theta =p+\tan 2 \theta\) then the value of \(\sin ^2 \theta\) in terms of p is given by _________
(A) \(\frac {(p-1)^2} {2 (p^2+1)}\)
(B) \(\frac 1 2 \Big( \frac {p-1} {p+1}\Big) ^2\)
(C) \(\frac {p^2-1} {2(p^2+1)}\)
(D) \(\frac {p^2-1} {2(p+1)^2}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A hollow convex lens made of glass will behave like a
(a) Convex lens
(b) concave lens
(c) glass plate
(d) mirror
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
(A) 0
(B) -16
(C) 16
(D) -11
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The number of common tangents to the circles \(x^2+y^2=4\) and \(x^2+y^2-6x-8y-24=0\) is__________
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 2
(D) 1
Given equation of circles are
\(x^2+y^2=4\)
whose radius =2
centre =(0,0)
and \(x^2+y^2-6x-8y-24=0\)
whose radius = \(\sqrt{9+16-24}=1\)
and centre =(3,4)
Now \(c_1c_2=\sqrt{(3-0)^2+(4-0)^2}=\sqrt{9+16}=5\)
\(a_1+a_2=2+1=3\)
\(c_1c_2>a_1+a_2\)
Number of common tangents=4

Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The number of ways of dividing 20 persons into 10 couples _____
(A) \(\frac {20!} {2^{10}}\)
(B) \(^{20} C_{10}\)
(C) \(\frac {20!} {(2!)^9}\)
(D) None of these
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
What is the hybridisation state of benzyl carbonium ion

(A) \(sp^3\)
(B) \(sp^2\)
(C) \(spd^2\)
(D) \(sp^2d\)
In the carbonium ion the carbon atom carrying the positive charge is \(sp^2\) hybridized
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A ray of light incident at an angle \(\theta\) on a refracting face of a prism emerges from the other face normally.If the angle of the prism is \(5^0\) and the prism is made of a material of refractive index 1.5,the angle of incidence is
(A) \(7.5^0\)
(B) \(5^0\)
(C) \(15^0\)
(D) \(2.5^0\)
Given that
\(A=5^0\)
\(\mu=1.5\)
\(i_2=0^0\)
\(r_2=0^0\)
We know that \(r_1+r_2=A\)
\(r_1=A-r_2=5-0=5^0\)
From Snell's law:
\(\mu=\frac {\sin i_1} {\sin r_1}\)
\(\sin i_1=\mu \sin r_1\\
=1.5\times \sin 5^0\\
=1.5\times 0.087=0.1305\\
=7.5^0\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A ray of light incident at an angle \(\theta\) on a refracting face of a prism emerges from the other face normally.If the angle of the prism is \(5^0\) and the prism is made of a material of refractive index 1.5,the angle of incidence is
(A) \(7.5^0\)
(B) \(5^0\)
(C) \(15^0\)
(D) \(2.5^0\)
Given that
\(A=5^0\)
\(\mu=1.5\)
\(i_2=0^0\)
\(r_2=0^0\)
We know that \(r_1+r_2=A\)
\(r_1=A-r_2=5-0=5^0\)
From Snell's law:
\(\mu=\frac {\sin i_1} {\sin r_1}\)
\(\sin i_1=\mu \sin r_1\\
=1.5\times \sin 5^0\\
=1.5\times 0.087=0.1305\\
=7.5^0\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Evaluate \(\displaystyle \int \frac {\sin x} {\sin (x-\alpha)} dx\)
(A) \(x \cos \alpha-\sin \alpha .\log |\sin (x-\alpha)|+C\)
(B) \(x \cos \alpha+\sin \alpha .\log |\sin (x-\alpha)|+C\)
(C) \(x \cos \alpha-x \sin \alpha .\log |\sin (x-\alpha)|+C\)
(D) \(\cos \alpha+x\sin \alpha .\log |\sin (x-\alpha)|+C\)
\(\displaystyle\int \frac {\sin x} {\sin (x-\alpha)} dx\) = \(\displaystyle\int \frac {\sin (x-\alpha +\alpha)} {\sin (x-\alpha)} dx\)
\(=\int [\cos \alpha +\sin \alpha .\cot (x-\alpha)] dx\)
\(=\int \cos \alpha +\sin \alpha .\int \cot (x-\alpha) dx\)
\(\cos \alpha \int dx+\sin \alpha \int \log|\sin (x-\alpha)|+C\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Evaluate \(\displaystyle\int _{-\frac {\pi} {2}}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} (\sin^3 x \cos x+\sin x \cos x)\:dx\)
(A) 2
(B) 0
(C)-1
(D) 1
\(f(x)= \sin^3 x \cos x+\sin x \cos x)\)
\(f(-x)= \sin^3 (-x) \cos(- x)+\sin (-x) \cos(- x)\)
\(=- \sin^3 x \cos x-\sin x \cos x\)
\(-f(x)\)
f is an odd function and because f is symmetric about origin over \(\Big[ -\frac {\pi} {2} ,\frac {\pi} {2}\Big]\)
\(\int _{-\frac {\pi} {2}}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} (\sin^3 x \cos x+\sin x \cos x)\:dx=0\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
What must be the power output of a rocket engine,which moves a 1,000 kg rocket at a constant speed of \(\)\(8.0\: m/s\)
(A) \(75\:kW\)
(B) \(79\:kW\)
(C) \(80\:kW\)
(D) \(81\:kW\)
The equation \(p=Fv\) with \(F=mg\)
solving \(p=mgv\) \(=(1,000 \:kg) (10 N/kg)\times (8.0\: m/s)\)
\(=80,000\:W=80\:kW\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Find the Point on the curve \(y=\sqrt{x}\) that is minimum distance from the point \((4,0)\)
(A) \(\Big(\frac {7} {4},\sqrt{\frac {7 }{4}}\Big)\)
(B) \(\Big(\frac {7} {5},\sqrt{\frac {7 }{5}}\Big)\)
(C) \(\Big(\frac {7} {2},\sqrt{\frac {7 }{2}}\Big)\)
(D) \(\Big(\frac {7} {4},\sqrt{\frac {2 }{7}}\Big)\)
Using the distance formula
\(D^2=(x-4)^2+(y-0)^2\)
\(=x^2-8x+16+y^2\)
Because \(y=\sqrt{x}\)
\(D^2=x^2-8x+16+x=x^2-7x+16\)
Let \(L=D^2\)
\(L=x^2-7x+16\)
Check first derivative test:\(\frac {dL} {dx}=2x-7=0\)
\(x=\frac {7} {2}\)
solving for y,\(y=\sqrt{\frac {7} {2}}\)
Check second derivative Test:\(\frac {d^2L} {dx^2}=2\)
The required Point is \(\Big(\frac {7} {2},\sqrt{\frac {7 }{2}}\Big)\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
which fuel would produce the largest mass of \(CO_2\) when \(10kg\) of the fuel undergo complete combustion?
(A) biodiesel,\(C_{17} H_{34} O_2\)
(B) ethanol,\(C_2H_6O\)
(C) Octane,\(C_8H_{18}\)
(D) Propane,\(C_3H_8\)
ethanol, mw 46 and 2 C’s to make 2 \(CO_2\)’s/ethanol
10kg of biodiesel is 10,000/270 = 37 moles, for 630 moles of \(CO_2\)
10kg of ethanol is 10,000/46 = 217 moles, for 434 moles of \(CO_2\)
10kg of propane is 10,000/44 = 227 moles, for 682 moles of \(CO_2\) so far the most…
10kg of octane is 10,000/114 = 88 moles, for 701 moles of \(CO_2\)
Octane makes the most \(CO_2\), at 30.8 kg, about 3 times the mass of the fuel.
Propane has higher H% at 18 vs 15 for octane
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Find the coefficient of \(x^3\) in the expansion \(\frac {3+x} {1+3x}\)
(A) -18
(B) -72
(C) -61
(D) -27
\(\frac {3+x} {1+3x}=(3+x) (1+3x)^{-1}\)
\((1+3x)^{-1}=1+(-1)(3x)+\frac {(-1) (-2) } {2\times 1} (3x)^2+\frac {(-1) (-2) (-3)} {3\times 2\times 1} (3x)^3+\cdots\)
\(=1-3x+9x^2-27x^3\)
\((3+x) (1+3x)^{-1}=(3+x) (1-3x+9x^2-27x^3+\cdots)\)
Term in \(x^3 \) is
\(3(-27x^3)+x(9x^2)=-72x^3\)
Coefficient of \(x^3 \) is -72
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A Loudspeaker connected to a signal generator produces a steady note of frequency \(256\:Hz\). A Observer moves towards the loudspeaker at a speed of \(25\:ms^{-1}\). Calculate the frequency of the sound that the observer hears.(speed of sound = \(330\:ms^{-1}\))
(A) \(277\)
(B) \(261\)
(C) \(292\)
(D) \(345\)
Relation between observed frequency and source is given by the formula
\(f_0=\frac {f_s v} {v\pm v_s}\)
where
\(f_0\rightarrow \text{observed frequency}\)
\(f_s\rightarrow \text{source frequency}\)
\(v_s\rightarrow \text{relative velcoity of source and observer}\)
\(f_0=\frac {256\times330} {330-25}=277\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Find the values of K for which the line \(2y=x+k\) forms a tangent to the curve \(y^2=2x\)
(A) 4
(B) 3
(C) 2
(D) 1
To find where the lines forms a tangent to the curve
Solving \(2y=x+k\cdots (1)\\ y^2=2x\cdots\cdots(2)\)
From (1) \(2y=x+k\) \(\Rightarrow\) \(x=2y-k\)
\(y^2=2(2y-k)\)
\(y^2=4y-2k\)
\(y^2-4y+2k=0\)
Compare with \(ax^2+bx+c=0\)
Condition: \(b^2-4ac=0\)
\((-4)^2-4\times1\times 2k=0\)
\(16-8k=0\)
\(k=2\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated