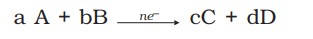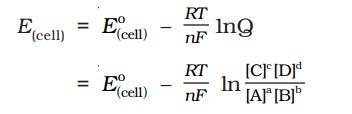Galvanic Cell
GALVANIC CELL
1.The cell which converts chemical energy to electrical energy is called Galvanic or Voltaic cell
2.Galvanic or Voltaic cell redox reaction is
\(\boxed{Zn_{(s)}+Cu_{(qq)}^{2+}\to Zn^{2+}_{(aq)}+Cu_{(s)}}\)
3.The example for Gavanic or Voltaic cell is Daniel cell
4.The cell notation of Daniel (Galvanic cell is
\(\boxed{Zn_{(s)}|Zn^{+2}_{(aq)} (C_1)|| Cu^{+2}_{(aq)}(C_2)|Cu_{(s)}}\)
5.EMF of the cell is calculated by
\(\boxed{E_{cell}=E_{right}-E_{left} (or) E_{cell}=E_{cathode}-E_{anode}}\)


Electrode Potential
A potential difference develops between the electrode and the electrolyte which is called electrode potential.
- In a galvanic cell, the half-cell in which oxidation takes place is called the anode, and it has a negative potential.
- Reduction takes place in the cathode, which has a positive potential with respect to the solution.
- The potential difference between the two electrodes of a galvanic cell is called the cell potential and is measured in volts. The cell potential is the difference between the electrode potentials (reduction potentials) of the cathode and anode, called the cell electromotive force (emf), calculated with -
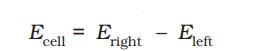


Standard Hydrogen Electrode
We arbitrarily choose the potential of one electrode (half-cell), then that of the other can be determined with respect to this. According to convention, a half-cell called the standard hydrogen electrode is assigned zero potential at all temperatures.

The electrode is dipped in an acidic solution, and pure hydrogen gas is bubbled through it.


Conductivity And Molar Conductivity
The flow of current in a solution is carried by ions. We quantify this with two key terms:
- Conductivity (K): The intrinsic ability of a solution to conduct electricity. It is the conductance of a 1m³ cube of solution. (Trend: Conductivity decreases upon dilution because there are fewer charge-carrying ions per unit volume.)
- Molar Conductivity: The conductivity of a solution per mole of electrolyte. It accounts for the number of ions. (Trend: Molar conductivity increases upon dilution. Ions are farther apart, reducing interference and increasing their mobility.)


Molar Conductivity In Weak And Strong Electrolytes
Strong Electrolytes: Dissociate completely. Molar conductivity increases slightly and linearly with dilution. We can extrapolate to find the limiting molar conductivity.
Weak Electrolytes: Dissociate partially. Molar conductivity increases steeply at low concentrations as dissociation increases, making extrapolation impossible.
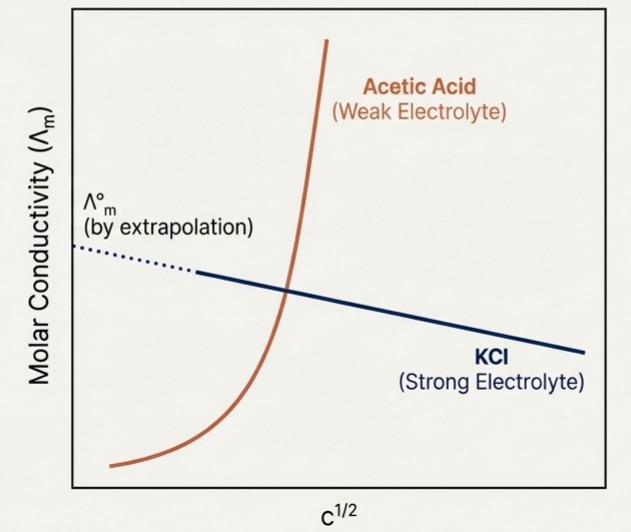


Kohlrausch's Law Of Independent Migration Of Lons
The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the individual limiting molar conductivities of its constituent ions:
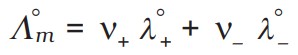
Application:
We can find the limiting molar conductivity for sodium chloride:
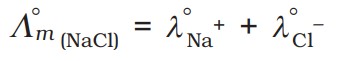


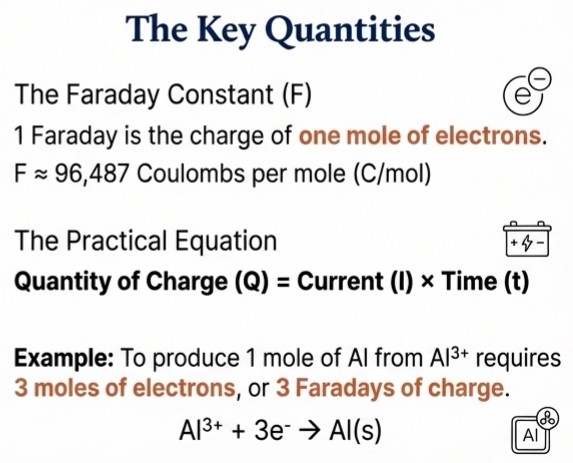
Faraday's Laws
First Law: The amount of substance produced at an electrode is directly proportional to the total quantity of electricity passed through the cell.
Second Law: For the same quantity of electricity, the amounts of different substances produced are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights.


Fuel Cells
Unlike batteries, fuel cells don't store energy; they convert it directly as long as fuel is provided.
Case Study: The Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell
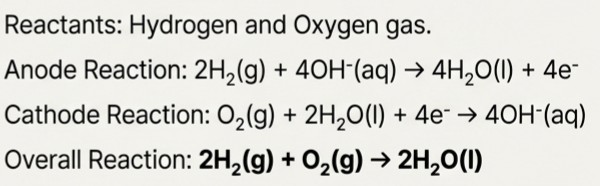
Key Advantages:
- High Efficiency: ~70% (vs. ~40% for thermal plants).
- Pollution-Free: The only product is water.


Corrosion
The rusting of iron is an electrochemical phenomenon that occurs in the presence of water and air.
- Anode (Oxidation): A spot on the iron surface.
- Fe(s) → Fe²*(aq) + 2e
- Cathode (Reduction): Electrons travel to another spot where oxygen is reduced.
- O2(g) + 4H*(aq) + 4e → 2H2O(l) Final Product: Fe2+ ions are further oxidised to form rust (hydrated ferric oxide, Fe2O3 · xH2O)
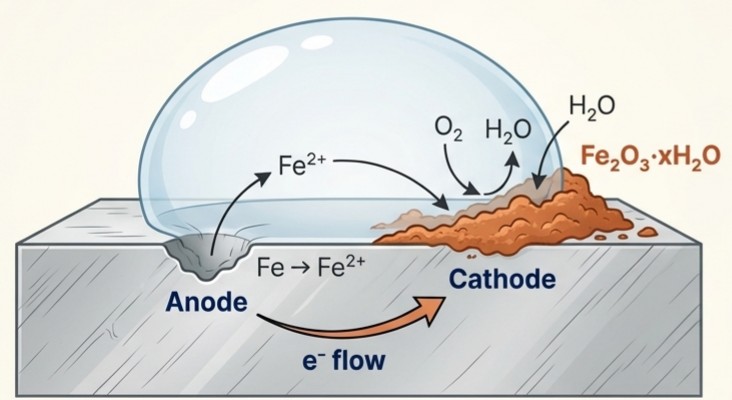
- Prevention: Understanding this process leads to prevention methods like painting, coating, or using a 'sacrificial electrode'.


 beeTokens
beeTokens